More about Art Gallery of Ontario

Contributor
The Art Gallery of Ontario features key Canadian works, a Gehry contribution, and a special guest appearance by Peter Paul Rubens.
One of the largest art museums in North America, the Art Gallery of Ontario plays host to a range of collections, from signature Canadian works by the Group of Seven and pre-Confederation Inuits to contemporary pieces by Cindy Sherman and Gerhard Richter. It was brought to life in 1900 by a small group of nine individuals and now holds more than 90,000 works of art in its collection.
In 2002, Ken Thomson (of the digital media empire, Thompson Co.) donated 2,000 artworks from his collection to the AGO. One of these artworks was a masterpiece by Peter Paul Rubens called The Massacre of the Innocents, which henceforth became the museum's most prized possession—and oft-repeated term on their About page.
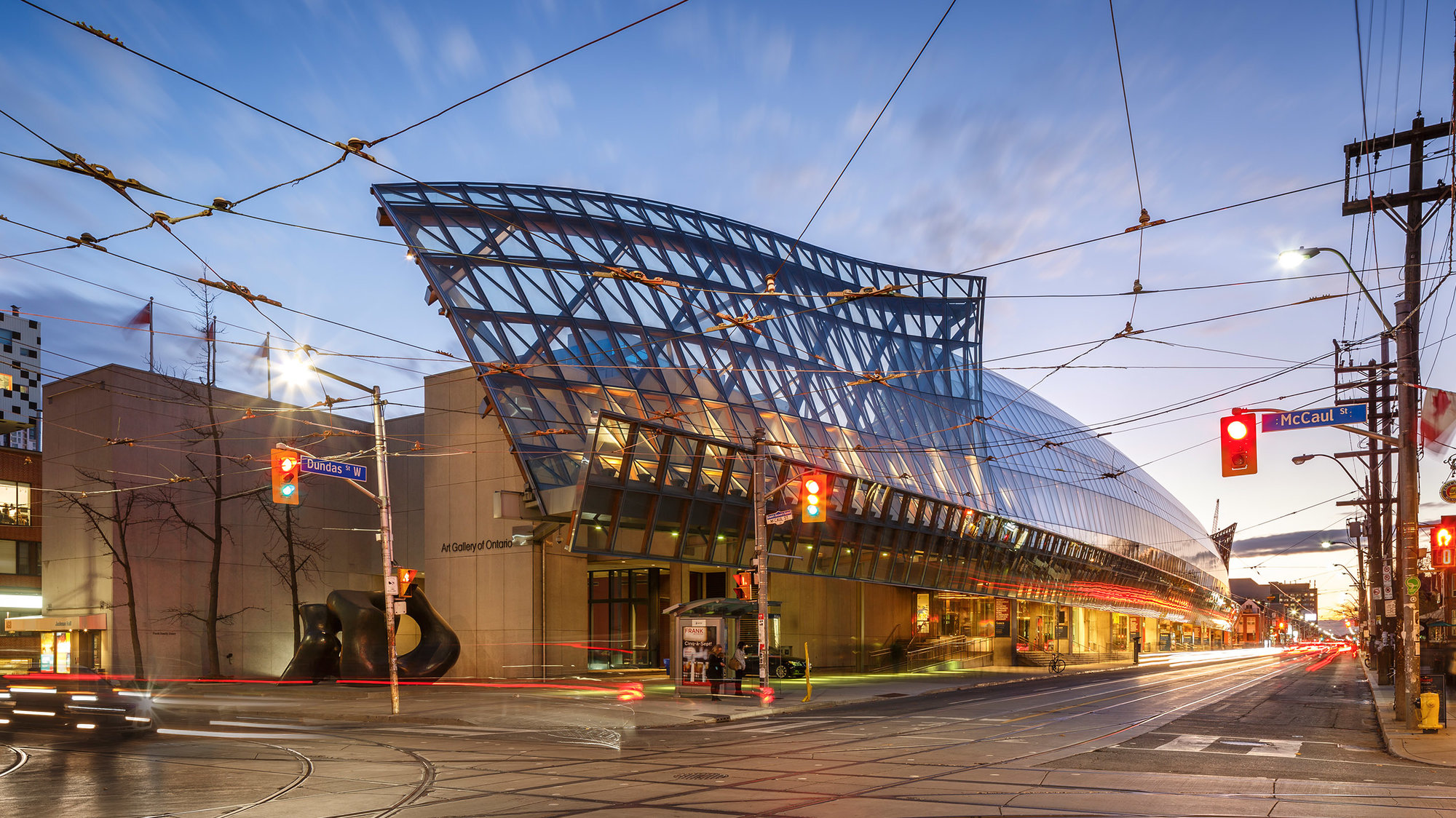
Since wealthy gifts beget wealthy rewards (for private institutions, at least), the AGO commissioned Frank Gehry to design an expansion to the museum that would house all of Thompson's fabulous collection. The Transformation AGO was completed in 2008 and opened to a deluge of architectural praise that, for Gehry, must have been old news by then. Highlights of the extension include a spiral staircase resembling poorly-served chocolate soft-serve and a gleaming hall of wood and glass the length of an entire city block.
Hopefully, though, you'll spend just as much time admiring the impressive combination of architectural mediums as you will their vast collection of artistic ones.
Sources
- "About the AGO." AGO Art Gallery of Ontario. http://www.ago.net/about-the-ago.
Featured Content
Here is what Wikipedia says about Art Gallery of Ontario
The Art Gallery of Ontario (AGO; French: Musée des beaux-arts de l'Ontario) is an art museum in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Located on Dundas Street West in the Grange Park neighbourhood of downtown Toronto, the museum complex takes up 45,000 square metres (480,000 sq ft) of physical space, making it one of the largest art museums in North America and the second-largest art museum in Toronto, after the Royal Ontario Museum. In addition to exhibition spaces, the museum also houses an artist-in-residence office and studio, dining facilities, event spaces, gift shop, library and archives, theatre and lecture hall, research centre, and a workshop.
Established in 1900 as the Art Museum of Toronto and formally incorporated in 1903, the museum was renamed the Art Gallery of Toronto in 1919, before adopting its present name, the Art Gallery of Ontario, in 1966. The museum acquired the Grange in 1911 and later undertook several expansions to the north and west of the structure. The first series of expansions occurred in 1918, 1924, and 1935, designed by Darling and Pearson. Since 1974, the gallery has undergone four major expansions and renovations. These expansions occurred in 1974 and 1977 by John C. Parkin, and 1993 by Barton Myers and KPMB Architects. From 2004 to 2008, the museum underwent another expansion by Frank Gehry. The museum complex saw further renovations in the 2010s by KPMB and Hariri Pontarini Architects.
The museum's permanent collection includes over 120,000 works spanning the first century to the present day. The museum collection includes a number works from Canadian, First Nations, Inuit, African, European, and Oceanic artists. In addition to exhibits for its collection, the museum has organized and hosted many travelling art exhibitions.
Check out the full Wikipedia article about Art Gallery of Ontario